OLVM: Upgrade from 4.4 to 4.5
Introduction VMware vSphere has long held the crown as the leading on-premises server virtualization solution across businesses of all sizes. Its ... Read More
Learn more about why Eclipsys has been named the 2023 Best Workplaces in Technology and Ontario, Certified as a Great Place to Work in Canada and named Canada’s Top SME Employer!
Learn more!Acronyms:
DG – Data Guard
OCI – Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
The most important part of the IT Infrastructure is having a proper Disaster Recovery plan. Organizations are spending colossal sums of money to have proper DR infrastructure. The best practice is to create your DR site in a different city or different geographical location. OCI provides greater flexibility to create DR within the same region or different region. Even small/medium scale companies can afford these DR sites. These OCI cloud features enable greater enhancement to infrastructure.
Furthermore, OCI provides Oracle Data Guard features to address DR (Disaster Recovery) situations. Data Guard enables and ensures high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery for your enterprise database.
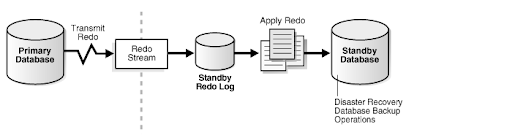
Oracle Data Guard provides an extensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to survive disasters (such as natural disasters) and data corruption.
Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as a cloned version of the production database and regularly applies changes from Primary Database to Standby Database. Then, if the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the primary role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
Active Data Guard: Active Data Guard enables read-only access to a physical standby database for queries, sorting, reporting, Web-based access, and so on, while continuously applying changes received from the primary database. In Active Data Guard standby database work as to be read-only with the apply state.
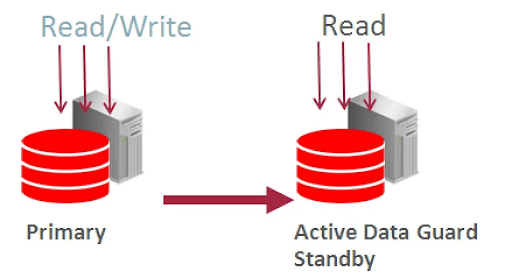
Note: For Active Data Guard, when you create the database, you need to select the Extreme Performance.
There are 4 different types of editions in Oracle Cloud:
Normal Data Guard: Normal Data Guard enables you to switch to the Standby Database when your primary database is down due to some outage or natural disasters. In Normal Data Guard, you can still open the standby database in read-mode but changes not applied while in read-only mode.
Types of DG: Physical | Logical | Snapshot
Creating DG in a cloud environment is now simplified to less than 4 clicks. In this article, I will cover how to create standby database within the same region.
First, navigate to the database and view the database. This shows the enabled Data Guard.
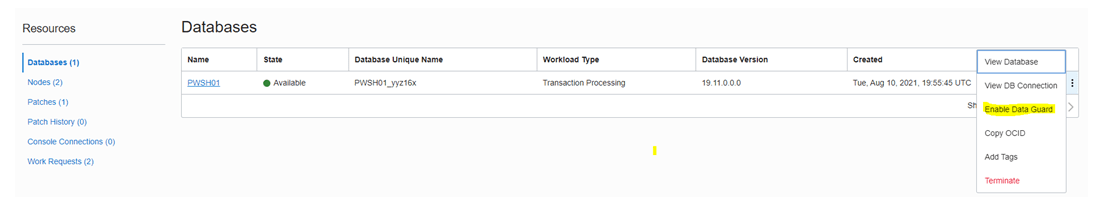
As per this figure we need the feed to Display Name, Region, and Availability Domain, etc.
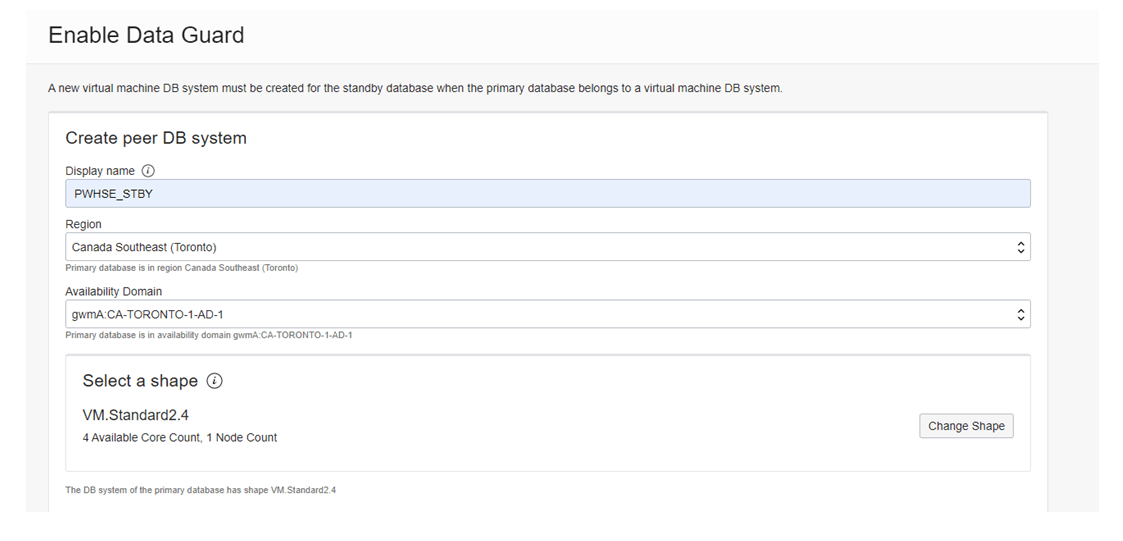
Next, select the required shape for the database server and provide hostname for the standby server.
It is important to select the correct network Virtual Cloud Network (VCN). We are creating this in the public segment to access this via internet.
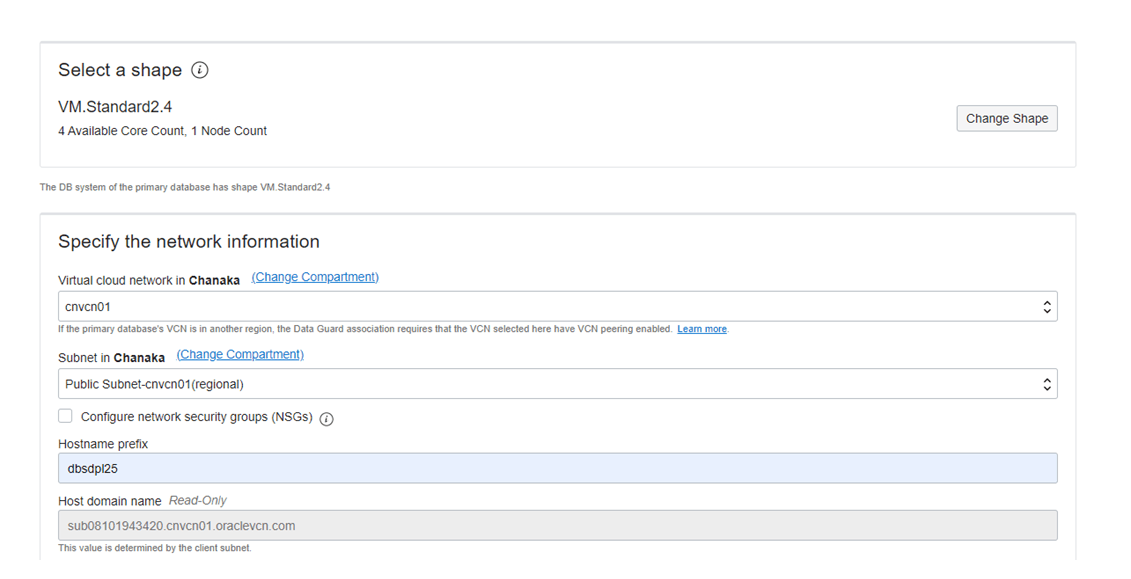
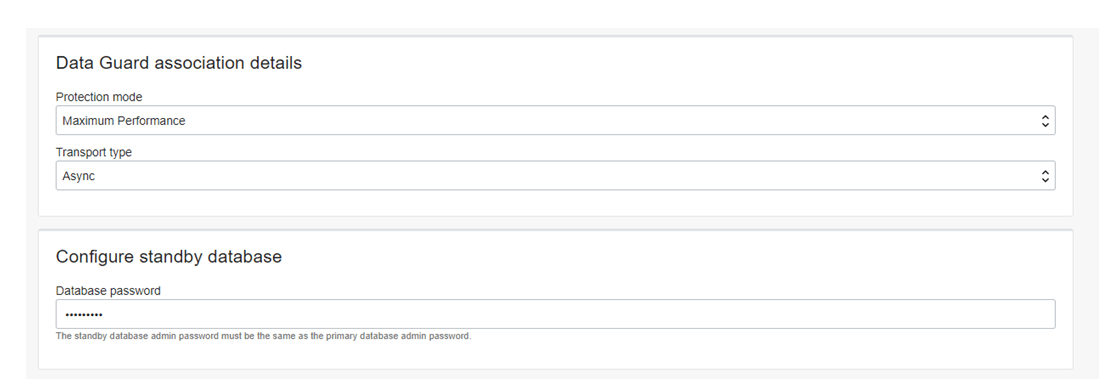
Next, select the database mode and transport mode. For this test, I’m selecting Maximum Performance and transport mode as Async.
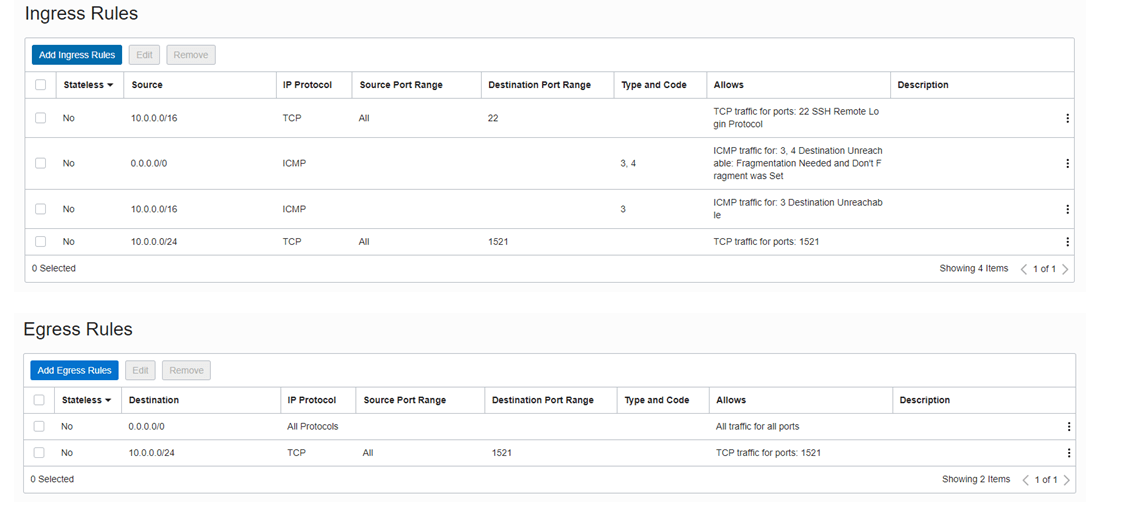
This error comes up when the port 1512 is not enabled for destination:
Data Guard Association cannot be created when standard database service port (1521) is
blocked for instances in
Subnet: ocid1.subnet.oc1.ca-toronto-1.aaaaaaaavkfa3xtnoyn4ce5l4g2ttgzf54lhkofaavnaoxiv3irog7ghkika
by security rules associated with
Subnet: ocid1.subnet.oc1.ca-toronto-1.aaaaaaaaceab2pepfsk54ektbyuvfl2rulk4d4luzbfu2iduyr7cmd2gwibq
To overcome this we need to create two rules: one for Ingress and another for Egress. Port 1512 should be available to communicate with standby server in region level.
Follow the same steps above to create the standby database.
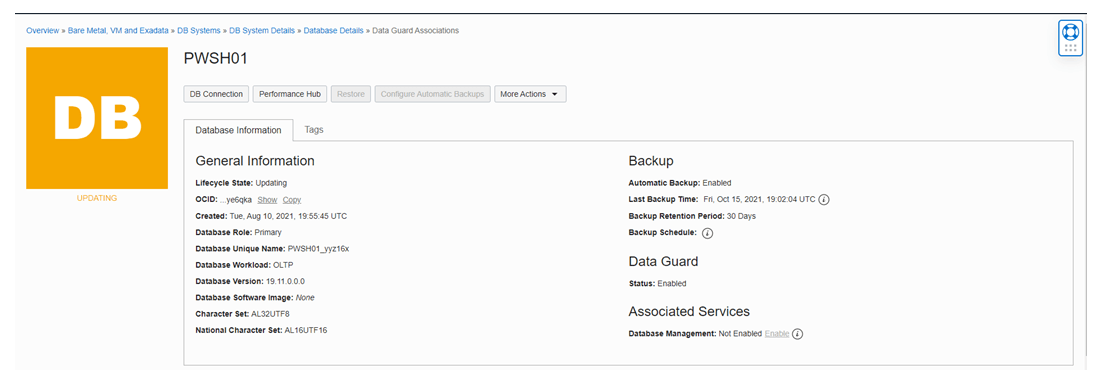
Once the provisioning is complete check the status from work request.
We can validate Data Guard status using dgmgrl utility. Also, it’s better to check the database role by login to database.
Database Role:
INSTANCE_NAME STATUS HOST_NAME STARTUP_TIME
---------------- ------------ ---------------------------------------------------------------- ----------------
PWSH011 MOUNTED dbsdpl251 26/10/2021 20:55
PWSH012 MOUNTED dbsdpl252 26/10/2021 20:55
SQL> select open_mode,database_role from gv$database;
OPEN_MODE DATABASE_ROLE
-------------------- ----------------
MOUNTED PHYSICAL STANDBY
MOUNTED PHYSICAL STANDBY
SQL>
DGMRRL Utility:
#### DG status
DGMGRL> show configuration;
Configuration - PWSH01_yyz16x_PWSH01_yyz1k6
Protection Mode: MaxPerformance
Members:
PWSH01_yyz16x - Primary database
PWSH01_yyz1k6 - Physical standby database
Fast-Start Failover: Disabled
Configuration Status:
SUCCESS (status updated 22 seconds ago)
DGMGRL> show database verbose 'PWSH01_yyz1k6';
Database - PWSH01_yyz1k6
Role: PHYSICAL STANDBY
Intended State: APPLY-ON
Transport Lag: 0 seconds (computed 0 seconds ago)
Apply Lag: 0 seconds (computed 0 seconds ago)
Average Apply Rate: 4.00 KByte/s
Active Apply Rate: 198.00 KByte/s
Maximum Apply Rate: 198.00 KByte/s
Real Time Query: ON
Instance(s):
PWSH011
PWSH012 (apply instance)Introduction VMware vSphere has long held the crown as the leading on-premises server virtualization solution across businesses of all sizes. Its ... Read More
Introduction Monitoring plays a major part in mission-critical environments. Most businesses depend on IT infrastructure. As the ... Read More