How to Delete Older Kernel Versions in Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
In Oracle Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), the conventional method for removing old kernels involves using the yum package manager. Here are the steps to accomplish this:
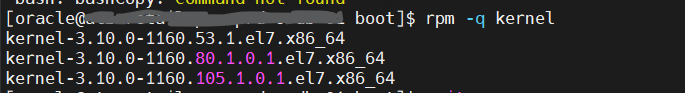
1. List Installed Kernels:First, you need to identify the installed kernels on your system using the rpm -q kernel command.
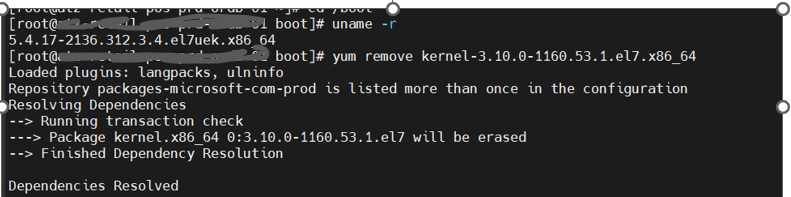
2. Remove Old Kernels:Once you’ve identified the kernels you want to remove, you can use yum to remove them. Make sure to keep at least one or two old kernels for backup purposes. Check the current kernel in use using the uname -r command. Then remove older kernels using the sudo yum remove kernel-OLD_VERSION
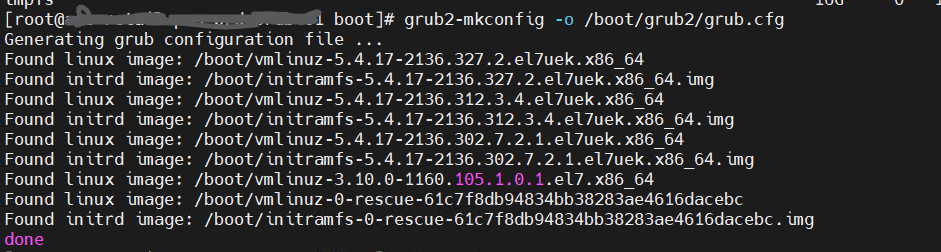
3. Update GRUB Configuration: After removing the kernels, it’s a good idea to update the GRUB bootloader configuration. sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg This command will regenerate the GRUB configuration file based on the new kernel configuration.
Conclusion: It is advisable to maintain at least one or two prior kernels on your system to serve as backups in case the latest kernel experiences any issues. Ensure you identify and remove the correct kernel packages, as deleting the wrong ones could lead to your system being unable to boot. Exercise caution whenever executing system-level operations.
More from this Author
The following steps can be taken to address the “ORA-19751: could not create the change tracking file” error when attempting to open the ... Read More
The procedure outlined below describes the steps to change the hostname of a Grid Infrastructure with Oracle Restart Configuration. This is typically ... Read More









