OCI FortiGate HA Cluster – Reference Architecture: Code Review and Fixes
Introduction OCI Quick Start repositories on GitHub are collections of Terraform scripts and configurations provided by Oracle. These repositories ... Read More
Découvrez pourquoi Eclipsys a été nommée 2023 Best Workplaces in Technology, Great Place to Work® Canada et Canada's Top 100 SME !
En savoir plus !After AWS, Oracle Cloud, and Azure, GCP (Google Cloud Platform) is the 4th cloud platform in our terraform tutorial series, we will describe what it takes to authenticate and provision a compute engine using their terraform provider. The instance will also have an Nginx website linked to its public IP. If you want to know about the differences GCP brings in terms of networking it’s wrapped up on my blog.
Note: GCP Terraform provider authentication was a hell to get hold on and counter-intuitive compared to other Cloud platforms. I wasted a lot of time just trying to figure if I could avoid hardcoding project id.
Here’s a direct link to my GitHub repo linked to this lab =>: terraform-examples/terraform-provider-gcp
Content:
I. Terraform Setup
IV. Partial Deployment
V. Full Deployment
Tips and Conclusion
The following illustration shows the layers involved between your workstation and GCP cloud while running the terraform actions along with the instance attributes we will be provisioning.
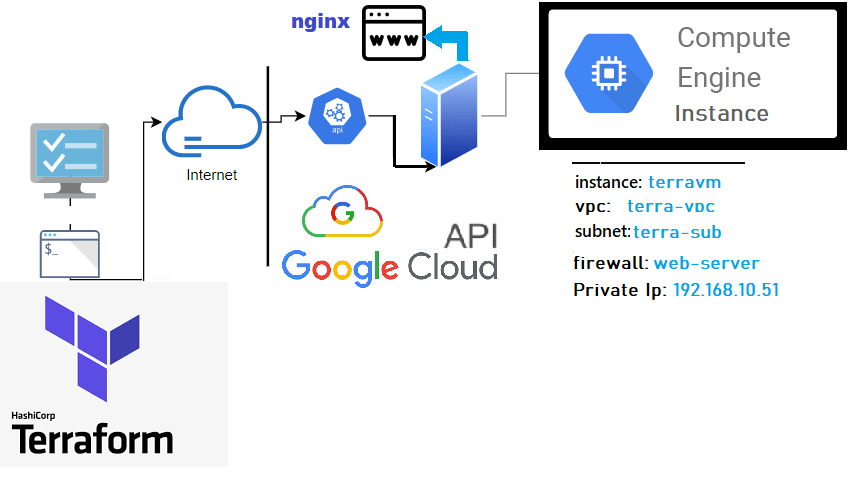
Besides describing my GitHub repo before starting this tutorial, I’ll just briefly discuss some principles.
– Can be a single file or split into multiple tf or tf.json files, any other file extension is ignored.
– Files are merged in alphabetical order but resource definition order doesn’t matter (subfolders are not read).
– Common configurations have 3 type of tf files and a statefile.
Terraform resource declaration syntax looks like this:
Component "Provider_Resource_type" "MyResource_Name" { Attribute1 = value ..
Attribute2 = value ..}Where do I find a good GCP deployment sample?
The easiest way is to create/locate an instance from the console and then use the import function from terraform to generate each of the related components in HCL format (VPC, instance,subnet,etc..) based on their id.
Example for a VPC >>
1- # vi vpc.tf
provider "google" {
features {}
}
resource "google_compute_network" "terra_vpc" {
}
2- # terraform import google_compute_network.terra_vpc {{project}}/{{name}}
3- # terraform show -no-color > vpc.tf Note:
If you want to import all the existing resources in your account in bulk mode terraformer can help import both code and state from your GCP account automatically.
Terraform Lab Content: I purposely split this lab in 2 for more clarity
I tried the lab using WSL (Ubuntu) terminal from windows but same applies to Mac.
Windows: Download and run the installer from their website (32-bit ,64-bit)
Linux: Download, unzip and move the binary to the local bin directory
$ wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/1.0.3/terraform_1.0.3_linux_amd64.zip
$ unzip terraform_1.0.3_linux_amd64.zip
$ mv terraform /usr/local/bin/$ terraform --version
Terraform v1.0.3GCP authentication (least user friendly)
To authenticate to GCP with Terraform you will need GCloud, service account credentials key file, and the projectId
Prerequisites
Using dedicated service accounts to authenticate with GCP is recommended practice (not user accounts or API keys)
$ gcloud auth login --activate …$ gcloud config list --format='table(account,project)' ACCOUNT PROJECT -------------- ------------- bdba@gmail.com brokedba2000
Service account: Either you create a service account with “owner role” in the console or run the below cli commands
1 -- Create service account
$ gcloud iam service-accounts create terraform-sa --display-name="Terra_Service"
$ gcloud iam service-accounts list --filter="email~terraform" --format='value(email)'
2 -- Bind it to a project and add owner role
$ gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID --member="serviceAccount:email" --role="roles/owner"
3 -– Generate the Key file for the service account
$ gcloud iam service-accounts keys create ~/gcp-key.json --iam-account=emailI’ll also assume the presence of an ssh key pair to attach to your VM instance. If not here is a command to generate a PEM based key pair.
$ ssh-keygen -P "" -t rsa -b 2048 -m pem -f ~/id_rsa_az
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Your identification has been saved in /home/brokedba/id_rsa_az.
Your public key has been saved in /home/brokedba/id_rsa_az.pub.
$ git clone https://github.com/brokedba/terraform-examples.gitNote: As explained earlier you will find 2 directories inside the repository which will make things easier:
terraform-provider-gcp/create-vpc/ To grasp how we deploy a single Vpc.terraform-provider-gcp/launch-instance/ For the final instance deploy.
terraform-provider-gcp/create-vpc” where our configuration resides (i.e vpc)$ cd /brokedba/gcp/terraform-examples/terraform-provider-gcp/create-vpc ”terraform init”.$ terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding latest version of hashicorp/google...
- Installing hashicorp/google v3.88.0...
* Installed hashicorp/google v3.88.0 (signed by HashiCorp)
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
$ terraform --version
Terraform v1.0.3 on linux_amd64
+ provider registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/google v3.88.0 ”create-vpc” directory. Here, only *.tf files matter (click to see content)$ tree
.
|-- outputs.tf ---> displays resources detail after the deploy
|-- variables.tf ---> Resource variables needed for the deploy
|-- vpc.tf ---> Our vpc terraform declaration
terraform plan command to create an execution plan (quick dry run to check the desired end-state).$ terraform plan
var.prefix The prefix used for all resources in this example
Enter a value: Demo
Terraform used selected providers to generate the following execution plan.
Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: + create
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# google_compute_network.terra_vpc will be created
+ resource "google_compute_firewall" "web-server"
{..
+ name = "allow-http-rule"
+ allow {
+ ports = [+ "80", + "22",+ "443",+ "3389",]
+ protocol = "tcp"
...
# google_compute_firewall.web-server will be created
+ resource "google_compute_firewall" "web-server" {
{..}
# google_compute_subnetwork.terra_sub will be created
+ resource "google_compute_subnetwork" "terra_sub"
{..
ip_cidr_range = ["192.168.10.0/24” ]
...}
Plan: 3 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
– The output being too verbose I deliberately kept only relevant attributes for the VPC resource plan
”terraform deploy” to provision the resources to create our VPC (listed in the plan)$ terraform apply -auto-approve
google_compute_network.terra_vpc: Creating...
google_compute_firewall.web-server: Creating...
google_compute_subnetwork.terra_sub: Creating...
...
Apply complete! Resources: 3 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
project = "brokedba2000"
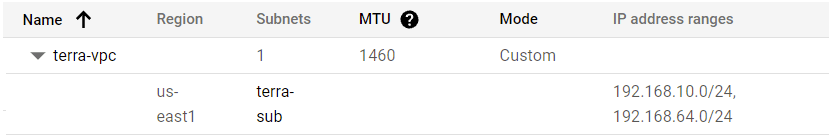
Observations:
– The deployment started by loading the resources variables in variables.tf which allowed the execution of vpc.tf
– Finally terraform fetched the attributes of the created resources listed in outputs.tf
Note: We’ll now destroy the VPC as the next instance deploy contains the same VPC specs.
$ terraform destroy -auto-approve
Destroy complete! Resources: 3 destroyed.
terraform-provider-gcp/launch-instance/$ tree ./terraform-provider-gcp/launch-instance
.
|-- cloud-init --> SubFolder
| `--> centos_userdata.txt --> script to config a webserver the Web homepage
| `--> sles_userdata.txt --> for SUSE
| `--> ubto_userdata.txt --> for Ubunto
| `--> el_userdata.txt --> for Enteprise linux distros
|-- compute.tf ---> Compute engine Instance terraform configuration
|-- outputs.tf ---> displays the resources detail at the end of the deploy
|-- variables.tf ---> Resource variables needed for the deploy
|-- vpc.tf ---> same vpc we deployed earlier
Note: As you can see we have 2 additional files and one Subfolder. compute.tf is where the compute instance and all its attributes are declared. All the other “.tf” files come from my VPC example with some additions for variables.tf and output.tf
...variable "user_data" { default = "./cloud-init/centos_userdata.txt"}
$ vi compute.tf
resource "google_compute_instance" "terravm" {
metadata = {
startup-script = ("${file(var.user_data)}")
... $ vi compute.tf resource "google_compute_instance" "terravm" { metadata = { admin_ssh_key { ssh-keys = var.admin":${file("~/id_rsa_gcp.pub")}" ## Change me
launch-instance” directory, you can run the plan command to validate the 9 resources required to launch our VM instance. The output has been truncated to reduce verbosity$ terraform plan
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Terraform will perform the following actions:
... # VPC declaration (see previous VPC deploy)
...
# google_compute_instance.terra_instance will be created
+ resource "google_compute_instance" "terra_instance" {
+ ...
+ hostname = "terrahost"
+ machine_type = "e2-micro"
+ name = "Terravm"
+ tags = [ + "web-server", ]
+ boot_disk {
+ initialize_params { + image = "centos-cloud/centos-7"
+ network_interface {
...
+ network_ip = "192.168.10.51"
}
+ metadata = {
+ "ssh-keys" = <<-EOT ssh-rsa AAAABxxx…*
EOT
+ "startup-script" = <<-EOT”
EOT}
# google_compute_address.internal_reserved_subnet_ip will be created
+ resource "google_compute_address" "internal_reserved_subnet_ip" {
...}
...
}
Plan: 5 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
$ terraform apply -auto-approve
...
google_compute_network.terra_vpc: Creating...
google_compute_firewall.web-server: Creating...
google_compute_subnetwork.terra_sub: Creating...
google_compute_address.internal_reserved_subnet_ip: Creating...
google_compute_instance.terra_instance: Creating...
Apply complete! Resources: 5 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
vpc_name = "terra-vpc"
Subnet_Name = "terra-sub"
Subnet_CIDR = "192.168.10.0/24"
fire_wall_rules = toset([
{…
"ports" = tolist([
"description" = "RDP-HTTP-HTTPS ingress trafic"
"destination_port_ranges" = toset([
"80",
"3389",
"443",
"3389",])
]
hostname = "terrahost.brokedba.com"
project = "brokedba2000"
private_ip = "192.168.10.51"
public_ip = "35.227.81.2"
SSH_Connection = "ssh connection to instance TerraCompute ==> sudo ssh -i ~/id_rsa_gcp centos@35.227.81.2"

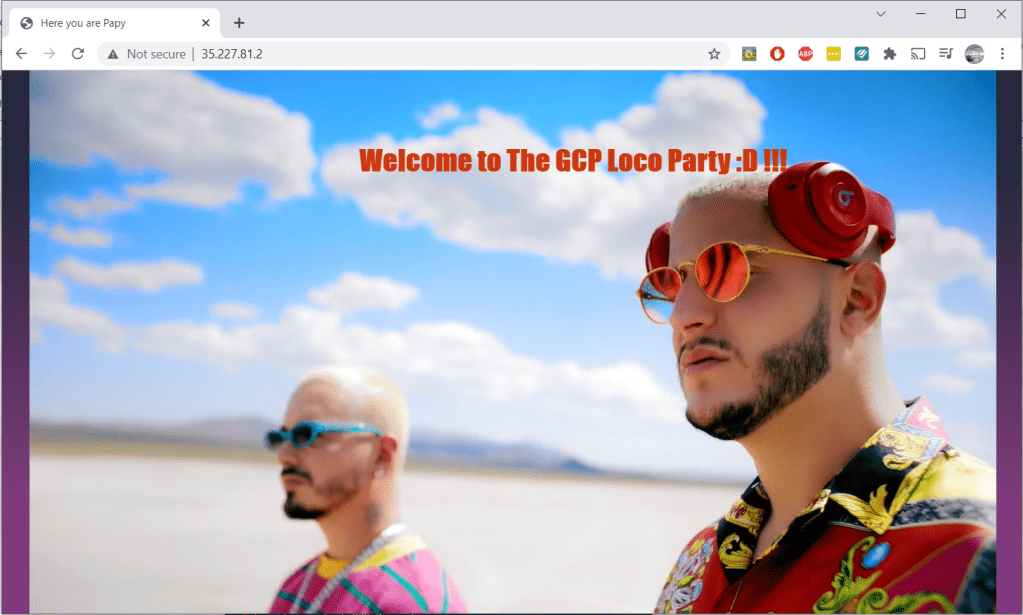
$ terraform output SSH_Connection
ssh connection to instance TerraCompute ==> sudo ssh -i ~/id_rsa_gcp centos@ ’public_IP’
variables.tf file.Thank you for reading!
Introduction OCI Quick Start repositories on GitHub are collections of Terraform scripts and configurations provided by Oracle. These repositories ... Read More
Introduction So far, I have used Oracle AutoUpgrade, many times in 3 different OS’. Yet the more you think you’ve seen it all and reached the ... Read More