Unified Auditing Housekeeping
Introduction Data is the new currency. It is one of the most valuable organizational assets, however, if that data is not well protected, it can ... Read More
Apprenez-en plus sur les raisons pour lesquelles Eclipsys a été certifié comme un excellent lieu de travail au Canada, les meilleurs lieux de travail en Ontario et en technologie, et a été nommé le meilleur employeur de PME au Canada pendant 3 ans !
En savoir plus !
Nowadays all the business markets are highly competitive and organizations want to take competitive advantages over others. When business is highly critical databases and application servers need to be up and running 24X7. Virtualization is the technology that helps to maximize the IT infrastructure cost. High availability of VM can be achieved easily from virtualization clustering. Also, Virtualization technology will ease the cloud migration journey.
Virtualization can be deployed in two ways
Below mentioned links are useful for getting a clear understanding of both types of deployment types.
Converged Deployment : https://www.bmc.com/blogs/converged-infrastructure-vs-hyper-converged-infrastructure/#:~:text=In%20a%20non%2Dconverged%20architecture,Network%2Dattached%20storage%20(NAS)
Hyperconverged:https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/hyperconverged-infrastructure/what-is-hyperconverged-infrastructure.
In a non-converged architecture, physical servers operate a virtualization hypervisor that manages each of the virtual machines (VMs) that have been created on the server. For data storage, there are typically three options:
With converged architecture, storage is attached directly to the physical server. Regular converged architecture can be just as fast (if not faster) than hyper-converged alternatives. In this setup, flash storage is almost always used. (The need for expensive SAN and NAS, in particular, is eliminated.)
Hyperconvergence is an approach to IT infrastructure that consolidates computing, storage, and networking resources into a unified system. A hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) consists of compute resources (virtual machines) managed with a hypervisor, software-defined storage, and software-defined networking. Hyperconvergence of virtualized resources allows you to manage your resources from a single, unified interface.
With software-defined computing and storage integrated together, you can reduce data center complexity and footprint and support more modern workloads with flexible architectures on industry-standard hardware.
There are a few prerequisites you need to understand before creating a cluster.
For optimal virtualization architecture, we need at least 3 nodes. Having 3 nodes will handle the fencing more efficiently than 2 nodes.
All depend on the capex cost, you can start with 2 nodes and plan to move 3 nodes within 2 years or so. There is no restriction that you cannot create an OLVM cluster with 2 nodes, but some of the fencing features will not work as expected.
Note: Make sure not to implement glusterfs with 2 nodes. Glusterfs hyper-converged architecture storage you need to have 3 nodes.
In this article, I will cover how to implement a shared fiber domain between two nodes.
As per Figure 1: Fiber LUN should be mapped to both the KVM nodes. In OLVM shared cluster SPM (Storage Pool Manager) Role will handle this shared storage mounting in both nodes.
Note: Make sure to map the same Fiber LUN to both nodes
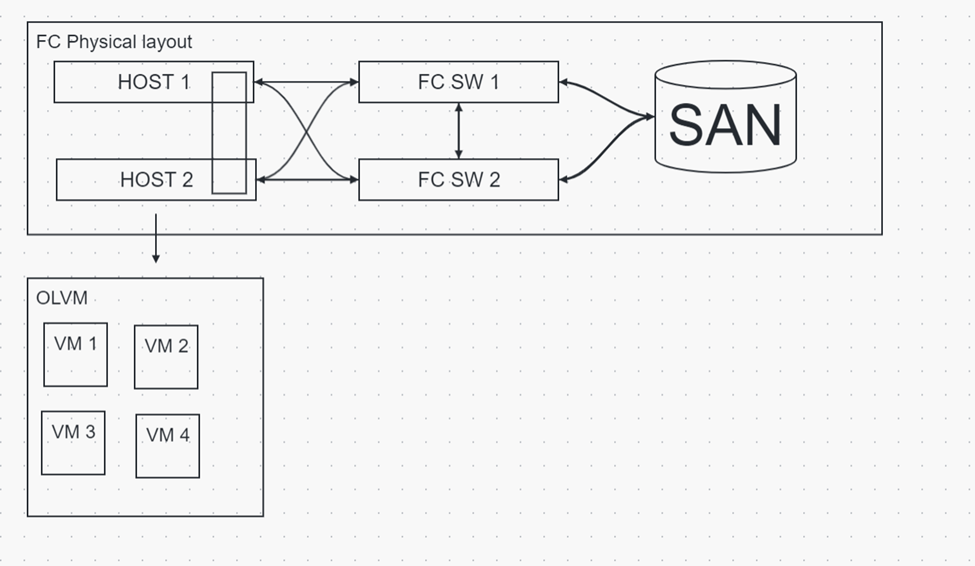
Figure 1: How to map the Fiber storage domain to both nodes
Mapping Fiber LUN to node01
[root@KVM01 ~]# lsblk | grep 3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c
└─3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c 252:2 0 200G 0 mpath
└─3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c 252:2 0 200G 0 mpath
└─3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c 252:2 0 200G 0 mpath
└─3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c 252:2 0 200G 0 mpath
[root@KVM120 ~]#
Mapping Fiber LUN to node02
[root@KVM02 ~]# lsblk | grep 3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c
└─3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c 252:2 0 200G 0 mpath
└─3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c 252:2 0 200G 0 mpath
└─3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c 252:2 0 200G 0 mpath
└─3624a93701561d6718da94a200001104c 252:2 0 200G 0 mpath
[root@KVM121 ~]#
Figure 2: Illustrates how to create a fiber channel data domain, Always double-check the LUN ID before selecting the disk. This will take 10min to create the lvm2 and the file structure.
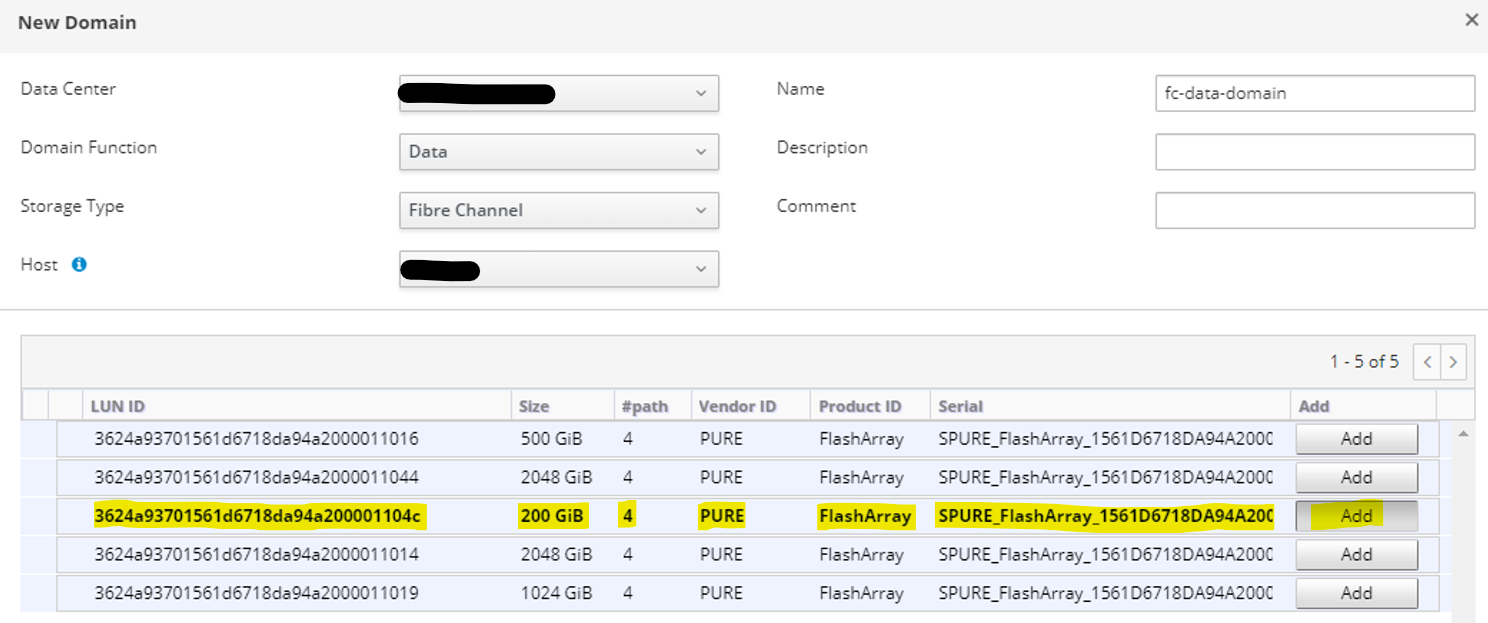
Figure 2: Add Fiber LUN as an FC-Data-Domain
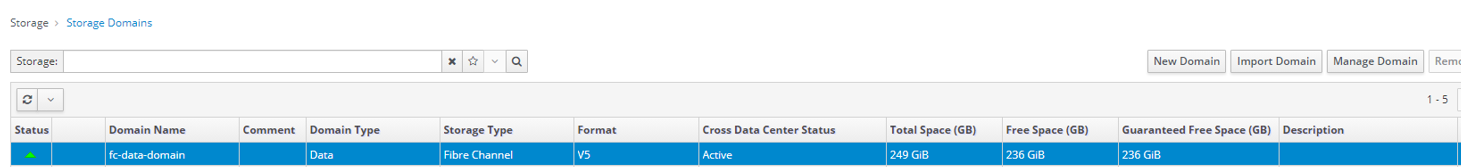
If this is created successfully, all 3 tasks will be completed with a green color taskbar.

Figure 3: OLVM Task Detail Tab
Once you successfully created the fc domain, the status will be displayed in green color in the storage section.
In summary, For two nodes not giving you the expected fencing results. When designing the OLVM architecture with gluster storage optimal results can be archived via 3 node architectures.
For two-node architectures, we can achieve OLVM environmental stability by implementing fiber channel storage domains. if you are still planning to have gluster storage, KVM must consist of 10G network cards. Also, we need to implement an arbitrator to avoid split brain.
Moving to fiber storage will completely eliminate the network traffic from the management network. OLVM SPM (Storage Pool Manager) will handle the mounting on both nodes. Also, fiber gives you enhanced performance on storage.
Introduction Data is the new currency. It is one of the most valuable organizational assets, however, if that data is not well protected, it can ... Read More
Introduction VMware vSphere has long held the crown as the leading on-premises server virtualization solution across businesses of all sizes. Its ... Read More